How the New Cyber Security Bill Will Strengthen UK Business Defences

How the New Cyber Security Bill Will Strengthen UK Business Defences – The Government Unveils New Data & Cyber Security Legislation in King’s Speech! In a Landmark Announcement, the Government has unveiled the new Cyber Security & Resilience Bill as part of the King’s Speech. This Legislation comes in response to the escalating Cyber Threats […]
The Government Unveils New Data & Cyber Security Legislation in King’s Speech!
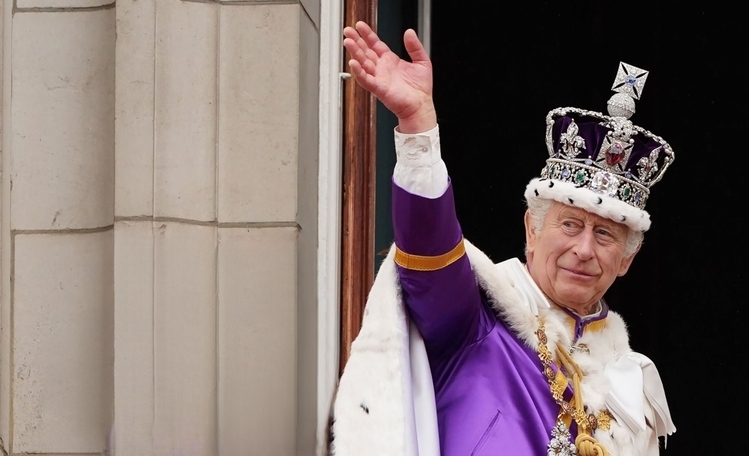

King Charles’s Speech yesterday the Introduction of the Cyber Security & Resilience Bill. This Bill aims to Enhance the UK’s Defenses against Cyber Threats by Establishing Stringent Regulations & Improving the Resilience of Critical Infrastructure. Cyber Security & Resilience Bill: Our Digital Economy is increasingly being attacked by Cyber Criminals & State Actors, affecting […]
Cyber Security Insights – Ransomware Defence Strategies in 2024

Ransomware has emerged as an insidious and relentless adversary in today’s digital landscape, leaving Individuals & Organisations grappling with the devastating consequences of their attacks. These malicious threats are designed to encrypt critical data and extort payment for its release, and over the years, they’ve evolved into increasingly sophisticated and disruptive forms. As we delve […]
Cyber Security Insurance Rates Fall as Businesses Improve Their Security

Cyber insurance premiums are falling globally as businesses become more adept in curbing their losses from cyber crime. Insurance premiums to protect companies against cyber attacks rocketed in 2021 and 2022, as the COVID-19 pandemic drove cyber incidents. But premiums have been dropping in the past year. The cyber insurance market saw double digit price […]
7 Common Security Attacks in The OSI Layer Model
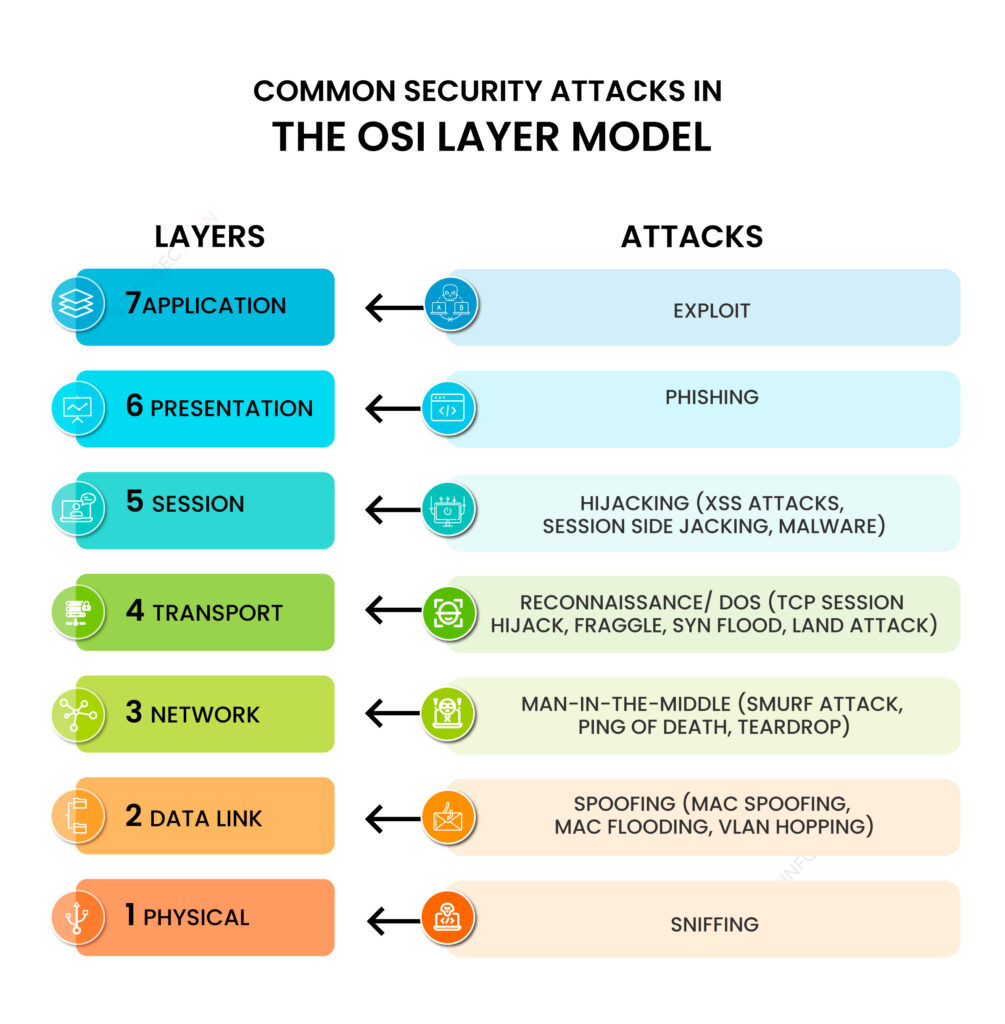
1) Sniffing attacks consist of intercepting data using a packet sniffer application. Then, if the captured packets are not encrypted, the packet sniffer can be used to read them. This allows attackers to analyze the network and gain information to corrupt it or even cause it to crash. 2) Spoofing attacks consist of a person or […]
New Phishing Campaign Deploys WARMCOOKIE Backdoor Targeting Job Seekers

Cybersecurity researchers have disclosed details of an ongoing phishing campaign that leverages recruiting- and job-themed lures to deliver a Windows-based backdoor named WARMCOOKIE. WARMCOOKIE appears to be an initial backdoor tool used to scout out victim networks and deploy additional payloads. The backdoor comes with capabilities to fingerprint infected machines, capture screenshots, and drop more […]
Uncovering High Street Bank’s Mobile App & Online Security Gaps

In today’s digital age, Online & Mobile Banking have become the norm for millions of customers in the UK. However, a recent 2024 Report by the respected consumer magazine “Which?” has raised alarming concerns about the security measures implemented by some of the country’s major high street banks. The report scrutinized the Mobile App & […]
Future EU Virtual Cybersecurity Center to Receive Secure Communication System From Indra

Spanish defense contractor Indra will integrate a secure communication system to withstand quantum computer attacks into the European Commission’s upcoming virtual cyber risk management center. The project is part of a 2023 program launched with a Leonardo-led consortium for new digital infrastructure with real-time tracking capability to protect against cyber criminal groups. The resulting solution […]
Lancaster University and National Cyber Force deliver ‘hackathon’

A University in Lancashire teamed up with the government’s National Cyber Force (NCF) to deliver a ‘hackathon’ event for the cyber experts of the future. The event, the first of its kind delivered by the NCF, saw some of the North West’s brightest young cyber talent put to the test at Lancaster University. Held within […]
Roku says more than 500,000 accounts impacted in Cyber Attack!

Streaming service provider Roku said on Friday it identified a second cyberattack that impacted about 576,000 additional accounts while investigating a breach that affected 15,000 user accounts earlier this year. The company, which had more than 80 million active accounts, said the hackers did not gain access to any sensitive information such as full credit […]


