Cyber Allies – Choosing The Right MSSP

Selecting the right Managed Security Service Provider (MSSP) is a pivotal decision for organisations seeking to bolster their Cyber Security Defences. In this Episode, we explore the Key Considerations & Strategic Approaches to ensure you choose an MSSP that aligns seamlessly with your unique security needs and overarching business objectives. Understanding Your Security Needs: Identifying Vulnerabilities: Conducting a Comprehensive Security Assessment is Foundational. According to the Ponemon Institute, organisations that regularly assess Vulnerabilities experience 40% fewer Security Incidents. Identifying weak points is crucial for an MSSP to tailor its services effectively. Defining Objectives: Clearly outlined security objectives are fundamental. A study by ISACA found that organisations with well-defined security objectives are 30% more successful in achieving their security goals. Whether it’s Compliance, Threat Detection or Risk Management, clear objectives guide MSSP selection. Evaluating MSSP Capabilities: Technological Expertise: MSSPs with advanced technological capabilities are essential. The Cyber Security Ventures Market Report predicts that global spending on Cyber Security will exceed £1Trillion from 2017 to 2021, emphasising the increasing reliance on advanced technologies. Ensure your MSSP leverages Innovative Tools, such as AI but also including Digital Forensics, Disaster Recovery & Backup Solutions, to stay ahead of Cyber Threats. Incident Response Time: Swift Incident Response is critical. The IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report indicates that organisations with an Incident Response team that can contain a breach in less than 30 Days save over £1Million compared to those taking longer. Assessing an MSSP’s Incident Response time is paramount for minimising the impact of Security Incidents. Digital Forensics: MSSPs should demonstrate proficiency in Digital Forensics, enabling them to investigate and analyse Security Incidents comprehensively. This capability ensures a thorough understanding of the nature and origin of Cyber Threats. Disaster Recovery and Backup: Robust Disaster Recovery & Backup Solutions are crucial components of MSSP capabilities. The ability to swiftly recover data and maintain business continuity in the face of disruptions is essential for minimising the impact of Cyber Incidents. Compliance & Industry Alignment: Regulatory Compliance: Regulatory fines for Non-Compliance can be substantial. The average cost of compliance for organisations is estimated to be £4.3Million, according to a Study by the Ponemon Institute. Choosing an MSSP that ensures compliance with Industry Regulations, such as the National Institute of Standards & Technology (NIST) Framework, safeguards against potential financial penalties. Industry Experience: Industry-specific knowledge enhances an MSSP’s effectiveness. Verizon’s Data Breach Investigations Report (DBIR) consistently highlights industry-specific threat patterns. An MSSP with experience in your sector is better equipped to address unique challenges, contributing to more effective Threat Mitigation. Scalability & Flexibility: Scalability: Scalable solutions are vital for adapting to organisational growth. The Cyber Security Market Report predicts that by 2025, global spending on Cyber Security Products & Services will exceed £1Trillion as organisations expand their security measures. Ensuring an MSSP’s services can scale alongside your growth guarantees ongoing effectiveness. Customisation: Tailored solutions enhance relevance. A study by Deloitte found that 66% of organisations believe Cyber Security Measures should be customised to their specific needs. An MSSP offering customisation ensures that security measures align precisely with your organisation’s requirements. Collaboration & Threat Intelligence Sharing: Collective Defence Mechanism: MSSPs actively participate in collaborative efforts to share Threat Intelligence. This collective approach enhances the Overall Defence Mechanism. According to the Cyber Threat Alliance, organisations participating in Threat Intelligence sharing experience a 64% Reduction in the time taken to Detect Threats. Rapid Adaptation to Emerging Threats: Collaborative threat intelligence sharing enables MSSPs to rapidly adapt to emerging Cyber Threats. A Study by Intel 471 found that 72% of organisations believe that Threat Intelligence sharing enhances their ability to understand and mitigate Cyber Threats effectively. Cross-Industry Insights: MSSPs collaborating with partners from various industries gain cross-industry insights. This broad perspective aids in anticipating and mitigating Threats that may not be sector-specific. A collaborative study by Symantec found that organisations sharing Threat Intelligence with Partners from different industries are better prepared for diverse Cyber Threats. MSSP Size Matters: Small & Local MSSP: Offer personalised service and understanding of regional Threats. A Cyber Security Insiders Report reveals that 62% of organisations believe local MSSPs provide a better understanding of Regional Cyber Threats. Mid-Sized MSSP: Mid-sized MSSPs combine expertise and flexibility. They are often more adaptable to unique organisational needs. A Gartner Report indicates that mid-sized MSSPs are growing at a rate of 15% Annually. Global Enterprise MSSP: Global MSSPs bring vast resources and a broad Threat Landscape Understanding. A Cybersecurity Ventures Projection estimates a 12% growth in spending on Global Enterprise MSSPs by 2025. Forging Strategic Partnerships: Choosing the right MSSP transcends mere Procurement; it’s about forging a strategic partnership. By aligning the MSSP’s capabilities with your organisation’s unique needs and objectives, and leveraging collaborative Threat Intelligence sharing, you establish the foundation for a robust and proactive Cyber Security Strategy. So Always Remember the Top Criteria for Choosing the Right MSSP are a Customised Solution alongside Stability. Excellent User Experience & Responsiveness. Cost-Effective mixed with Strong Organisational Effectiveness. The right Technology & Expertise!
MSSPs: Cyber Allies – Choosing The Right MSSP

Selecting the right Managed Security Service Provider (MSSP) is a pivotal decision for organisations seeking to bolster their Cyber Security Defences. In this Episode, we explore the Key Considerations & Strategic Approaches to ensure you choose an MSSP that aligns seamlessly with your unique security needs and overarching business objectives. Understanding Your Security Needs: Identifying Vulnerabilities: Conducting a Comprehensive Security Assessment is Foundational. According to the Ponemon Institute, organisations that regularly assess Vulnerabilities experience 40% fewer Security Incidents. Identifying weak points is crucial for an MSSP to tailor its services effectively. Defining Objectives: Clearly outlined security objectives are fundamental. A study by ISACA found that organisations with well-defined security objectives are 30% more successful in achieving their security goals. Whether it’s Compliance, Threat Detection or Risk Management, clear objectives guide MSSP selection. Evaluating MSSP Capabilities: Technological Expertise: MSSPs with advanced technological capabilities are essential. The Cyber Security Ventures Market Report predicts that global spending on Cyber Security will exceed £1Trillion from 2017 to 2021, emphasising the increasing reliance on advanced technologies. Ensure your MSSP leverages Innovative Tools, such as AI but also including Digital Forensics, Disaster Recovery & Backup Solutions, to stay ahead of Cyber Threats. Incident Response Time: Swift Incident Response is critical. The IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report indicates that organisations with an Incident Response team that can contain a breach in less than 30 Days save over £1Million compared to those taking longer. Assessing an MSSP’s Incident Response time is paramount for minimising the impact of Security Incidents. Digital Forensics: MSSPs should demonstrate proficiency in Digital Forensics, enabling them to investigate and analyse Security Incidents comprehensively. This capability ensures a thorough understanding of the nature and origin of Cyber Threats. Disaster Recovery and Backup: Robust Disaster Recovery & Backup Solutions are crucial components of MSSP capabilities. The ability to swiftly recover data and maintain business continuity in the face of disruptions is essential for minimising the impact of Cyber Incidents. Compliance & Industry Alignment: Regulatory Compliance: Regulatory fines for Non-Compliance can be substantial. The average cost of compliance for organisations is estimated to be £4.3Million, according to a Study by the Ponemon Institute. Choosing an MSSP that ensures compliance with Industry Regulations, such as the National Institute of Standards & Technology (NIST) Framework, safeguards against potential financial penalties. Industry Experience: Industry-specific knowledge enhances an MSSP’s effectiveness. Verizon’s Data Breach Investigations Report (DBIR) consistently highlights industry-specific threat patterns. An MSSP with experience in your sector is better equipped to address unique challenges, contributing to more effective Threat Mitigation. Scalability & Flexibility: Scalability: Scalable solutions are vital for adapting to organisational growth. The Cyber Security Market Report predicts that by 2025, global spending on Cyber Security Products & Services will exceed £1Trillion as organisations expand their security measures. Ensuring an MSSP’s services can scale alongside your growth guarantees ongoing effectiveness. Customisation: Tailored solutions enhance relevance. A study by Deloitte found that 66% of organisations believe Cyber Security Measures should be customised to their specific needs. An MSSP offering customisation ensures that security measures align precisely with your organisation’s requirements. Collaboration & Threat Intelligence Sharing: Collective Defence Mechanism: MSSPs actively participate in collaborative efforts to share Threat Intelligence. This collective approach enhances the Overall Defence Mechanism. According to the Cyber Threat Alliance, organisations participating in Threat Intelligence sharing experience a 64% Reduction in the time taken to Detect Threats. Rapid Adaptation to Emerging Threats: Collaborative threat intelligence sharing enables MSSPs to rapidly adapt to emerging Cyber Threats. A Study by Intel 471 found that 72% of organisations believe that Threat Intelligence sharing enhances their ability to understand and mitigate Cyber Threats effectively. Cross-Industry Insights: MSSPs collaborating with partners from various industries gain cross-industry insights. This broad perspective aids in anticipating and mitigating Threats that may not be sector-specific. A collaborative study by Symantec found that organisations sharing Threat Intelligence with Partners from different industries are better prepared for diverse Cyber Threats. MSSP Size Matters: Small & Local MSSP: Offer personalised service and understanding of regional Threats. A Cyber Security Insiders Report reveals that 62% of organisations believe local MSSPs provide a better understanding of Regional Cyber Threats. Mid-Sized MSSP: Mid-sized MSSPs combine expertise and flexibility. They are often more adaptable to unique organisational needs. A Gartner Report indicates that mid-sized MSSPs are growing at a rate of 15% Annually. Global Enterprise MSSP: Global MSSPs bring vast resources and a broad Threat Landscape Understanding. A Cybersecurity Ventures Projection estimates a 12% growth in spending on Global Enterprise MSSPs by 2025. Forging Strategic Partnerships: Choosing the right MSSP transcends mere Procurement; it’s about forging a strategic partnership. By aligning the MSSP’s capabilities with your organisation’s unique needs and objectives, and leveraging collaborative Threat Intelligence sharing, you establish the foundation for a robust and proactive Cyber Security Strategy.
Top 5 Regulatory Changes Shaping Cyber Security in 2024

As the Regulatory environment becomes increasingly stringent, the importance of being prepared for these changes cannot be overstated. Failure to comply with New Regulations can result in severe financial penalties, reputational damage and increased vulnerability to Cyber Threats. Proactive measures and timely compliance are not just Regulatory necessities; they are essential to safeguarding your organisation’s assets and maintaining competitive advantage. In 2023 alone, Regulatory Fines related to Cyber Security Compliance amounted to over £1.6 Billion Globally, with the average cost of a data breach reaching £3.4 Million. Organisations that fail to meet compliance standards not only face these financial burdens but also risk losing customer trust. Studies show that 60% of consumers are less likely to do business with companies that have suffered a data breach. Moreover, the reputational damage can lead to a significant loss in market share, as well as increased scrutiny from Regulators & Investors. Staying ahead of regulatory changes and implementing robust security measures can therefore save your organisation from these costly consequences. Top 5 Regulatory Changes Shaping Cyber Security in 2024: Staying ahead in Cyber Security requires not just awareness but strategic action. Here are the Top Five Regulatory Changes you need to know: NIS 2 Directive: New Requirements for Cyber Security Measures with hefty fines for Non-Compliance. Cyber Security & Resilience Bill: Expanded Scope of NIS Regulations & Mandatory Ransomware Reporting. NCSC Advisory on APT40: Insights into State-Sponsored Threats from China to Bolster Your Defences. DORA Regulations: New Standards for Managing ICT Risks in the Financial Sector. EU AI Act: Obligations for Developing Secure AI Systems, Focusing on Preventing Cyber Attacks. Conclusion: As regulatory landscapes shift, it is crucial for organisations to stay informed and proactive. Ensuring compliance with new and upcoming regulations not only avoids hefty fines but also strengthens overall Cyber Security Posture. Stay ahead of the curve by implementing robust security measures and preparing for these significant regulatory changes.
How the New Cyber Security Bill Will Strengthen UK Business Defences

How the New Cyber Security Bill Will Strengthen UK Business Defences – The Government Unveils New Data & Cyber Security Legislation in King’s Speech! In a Landmark Announcement, the Government has unveiled the new Cyber Security & Resilience Bill as part of the King’s Speech. This Legislation comes in response to the escalating Cyber Threats faced by our Digital Economy & Critical Infrastructure. Over the past 18 Months, vital Services such as Hospitals, Universities, Local Authorities & Government Departments have been targeted by Cyber-Attacks. These attacks, which have affected institutions like the NHS & The Ministry of Defence, highlight the severe risks our essential services face from hostile actors. To address these vulnerabilities and safeguard our Digital Economy, the Bill aims to fortify the UK’s Cyber Defences and ensure the security of Critical Infrastructure & Digital Services relied upon by businesses. What Does The Bill Do? The Cyber Security & Resilience Bill introduces several crucial updates to enhance the UK’s Cybersecurity Framework: Expanded Scope: The Bill extends the remit of existing regulations to cover a broader range of digital services and supply chains, recognising the growing threat vector posed by these areas. It seeks to address gaps exposed by recent high-profile attacks, such as the Ransomware Incident affecting London Hospitals. Strengthened Regulators: Regulators will receive enhanced powers to enforce Cybersecurity measures, including potential cost recovery mechanisms to bolster resources. The Bill empowers regulators to proactively investigate vulnerabilities and ensure that essential Cyber Safety Measures are implemented. Increased Incident Reporting: The Bill mandates more detailed incident reporting, providing the Government with better data on Cyber-Attacks. This will improve our understanding of the threat landscape and enhance response strategies, particularly for cases involving ransom demands. Territorial Extent: The Bill will apply UK-wide, ensuring consistent protection across the entire country. Key Facts: The current Cyber Security Regulations play an essential role in safeguarding the UK’s Critical National Infrastructure by placing security duties on industry involved in the delivery of essential services. The Regulations cover Five Sectors (Transport, Energy, Drinking Water, Health & Digital Infrastructure) and some digital services (including Online Marketplaces, Online Search Engines & Cloud Computing Services). Twelve Regulators (competent Authorities) are responsible for implementing the Regulations. Hostile Cyber Actors are increasingly targeting our Critical Sectors & Supply Chains. Recent serious high-profile attacks impacting London Hospitals, and the Ministry of Defence as well as Ransom Attacks on the British Library & Royal Mail, have highlighted that our Services & Institutions are vulnerable to attack. The impacts of a Cyber-Attack on these Sectors pose severe risks to UK Citizens, Core Services and the Economy at large. For example, as a result of the Ransomware Attack affecting the NHS in England in June, 3,396 Outpatient Appointments and 1,255 elective procedures were postponed across King’s College Hospital and Guy’s & St Thomas’ Hospital. The total cost of Cyber-Attacks to the UK was estimated at £27 Billion per annum in 2011, this figure is likely to have increased. National Cyber Security Centre assess that the increased threat from Hostile States & State-Sponsored Actors continues to ramp up. At a recent Speech at Cyber UK, the National Cyber Security Centre CEO Felicity Oswald warned that providers of essential services in the UK cannot afford to ignore these threats. Implications: The Cyber Security & Resilience Bill, alongside the Digital Information & Smart Data Bill, signifies the UK’s commitment to advancing its data and technology economies while bolstering Cybersecurity Protections. Businesses, particularly those in Technology & Critical Infrastructure Sectors, will need to enhance their Cyber Defences to comply with New Regulations and safeguard against emerging threats. Conclusion: The Introduction of the Cyber Security & Resilience Bill marks a significant advancement in the UK’s approach to protecting its Digital Infrastructure. As the Government strengthens its Cybersecurity framework, businesses across all sectors will face new demands for robust Cyber Defences & Regulatory Compliance. This evolving landscape underscores the critical need for skilled Cybersecurity Professionals who can navigate these complex challenges.
The Government Unveils New Data & Cyber Security Legislation in King’s Speech!

King Charles’s Speech yesterday the Introduction of the Cyber Security & Resilience Bill. This Bill aims to Enhance the UK’s Defenses against Cyber Threats by Establishing Stringent Regulations & Improving the Resilience of Critical Infrastructure. Cyber Security & Resilience Bill: Our Digital Economy is increasingly being attacked by Cyber Criminals & State Actors, affecting essential Public Services & Infrastructure. In the last 18 Months, our Hospitals, Universities, Local Authorities, Democratic Institutions & Government Departments have been targeted in Cyber-Attacks. Our Essential Services are vulnerable to Hostile Actors and recent Cyber-Attacks affecting the NHS & Ministry of Defence show the impacts can be severe. We need to take swift action to address vulnerabilities and protect our Digital Economy to deliver growth. The Bill will strengthen the UK’s Cyber Defences, ensure that Critical Infrastructure & Digital Services that companies rely on are secure. What Does The Bill Do? The Bill will strengthen our defences and ensure that more essential Digital Services than ever before are protected, for example by expanding the remit of the existing Regulation, putting Regulators on a stronger footing, and increasing reporting requirements to build a better picture in government of Cyber Threats. The existing UK Regulations reflect law inherited from the EU and are the UK’s only cross-sector Cyber Security Legislation. They have now been superseded in the EU and require urgent update in the UK to ensure that our Infrastructure & Economy is not comparably more vulnerable. The Bill will make crucial updates to the Legacy Regulatory Framework by: Expanding the remit of the regulation to protect more digital services and supply chains. These are an increasingly attractive threat vector for attackers. This Bill will fill an immediate gap in our defences and prevent similar attacks experienced by critical Public Services in the UK, such as the recent ransomware attack impacting London Hospitals. Putting Regulators on a strong footing to ensure essential Cyber Safety Measures are being implemented. This would include potential cost recovery mechanisms to provide resources to Regulators and providing powers to proactively investigate potential vulnerabilities. Mandating increased incident reporting to give government better data on Cyber-Attacks, including where a company has been held to ransom – this will improve our understanding of the threats and alert us to potential attacks by expanding the type and nature of incidents that regulated entities must report. Territorial Extent & Application – The Bill will extend and apply UK-Wide. Key Facts: The current Cyber Security Regulations play an essential role in safeguarding the UK’s Critical National Infrastructure by placing security duties on industry involved in the delivery of essential services. The Regulations cover Five Sectors (Transport, Energy, Drinking Water, Health & Digital Infrastructure) and some digital services (including Online Marketplaces, Online Search Engines & Cloud Computing Services). Twelve Regulators (competent Authorities) are responsible for implementing the Regulations. Hostile Cyber Actors are increasingly targeting our Critical Sectors & Supply Chains. Recent serious high-profile attacks impacting London hospitals, and the Ministry of Defence as well as ransom attacks on the British Library & Royal Mail, have highlighted that our Services & Institutions are vulnerable to attack. The impacts of a Cyber-Attack on these sectors pose severe risks to UK Citizens, Core Services and the Economy at large. For example, as a result of the Ransomware Attack affecting the NHS in England in June, 3,396 Outpatient Appointments and 1,255 elective procedures were postponed across King’s College Hospital and Guy’s & St Thomas’ Hospital. The total cost of Cyber-Attacks to the UK was estimated at £27 Billion per annum in 2011, this figure is likely to have increased. National Cyber Security Centre assess that the increased threat from hostile states and state-sponsored actors continues to ramp up. At a recent speech at CyberUK, National Cyber Security Centre CEO Felicity Oswald warned that providers of essential services in the UK cannot afford to ignore these threats. Two Post-Implementation Reviews found the original Regulations are having a positive impact, but that progress has not been fast enough. In 2022, the Review found that they ‘are a vital framework in raising wider UK resilience against Network & Information Systems Security Threats’, but updates are required to keep pace with growing threats. Just over half of operators of essential services have updated or strengthened existing policies and processes since the inception of the Regulations in 2018.
Cyber Security Insights – Ransomware Defence Strategies in 2024

Ransomware has emerged as an insidious and relentless adversary in today’s digital landscape, leaving Individuals & Organisations grappling with the devastating consequences of their attacks. These malicious threats are designed to encrypt critical data and extort payment for its release, and over the years, they’ve evolved into increasingly sophisticated and disruptive forms. As we delve into the strategies to defend against these digital blackmailers, it’s essential to understand the broader context in which they operate. During the last 12 Months Ransomware Attacks have witnessed an alarming 93% Increase, making them one of the most prevalent Cyber Threats globally. Moreover, the average Ransom Payment per incident has skyrocketed to an eye-watering £2.5Million, underlining the growing financial impact of these attacks and the urgent need to fortify our defences. 1. Robust Backups: A Vital Shield Maintaining regular, secure, and segmented backups of critical data remains a robust defence against Ransomware Attacks. Backups should be comprehensive, including all essential data, and should be tested regularly to ensure their reliability and completeness. A well-executed Backup Strategy ensures that, in the event of an attack, data can be quickly restored, mitigating the impact and minimising downtime. 2. Vigilant Employee Training One of the most formidable defences against Ransomware is an educated and vigilant workforce. Employees need to be trained to recognise Phishing Attempts, Suspicious Links & Questionable Email Attachments. By empowering your team to promptly report anomalies and potential threats, you create a culture of Cyber Awareness and resilience within your Organisation. 3. Software Updates & Patch Management Ransomware Attackers often exploit known Vulnerabilities in Outdated Software. Frequent Updates of software and operating systems, coupled with diligent Patch Management, are pivotal. Ensuring that your systems are up-to-date with the latest Patches helps minimise Vulnerabilities and strengthens your defences against potential exploits. 4. Deploy Advanced Security Solutions Utilising sophisticated Security Software, such as Endpoint Protection, Intrusion Detection Systems & Advanced Firewalls, provides an additional layer of defence against Ransomware. These solutions can identify, isolate, and contain threats before they escalate, enhancing your Organisation’s Overall Security Posture. 5. Incident Response & Recovery Plan In the unfortunate event of a Ransomware Attack, a Comprehensive Incident response Plan is invaluable. This plan outlines the steps to be taken, including Containment, Communication, Recovery Procedures & Legal Considerations. A well-defined plan minimises downtime and reduces the overall impact of an attack. 6. Collaborative Partnerships & Threat Intelligence Sharing Engaging in Collaborative Partnerships, sharing Threat Intelligence, and staying informed about Emerging Threats are key in the fight against Ransomware. Participation in a Network that shares information on Ransomware Trends & Potential Threats provides valuable insights and proactive measures to mitigate risks. The stark reality is that the fight against Ransomware is an ongoing battle. Ransomware Attackers are relentless, and their tactics continually evolve. In this landscape, a proactive and multi-faceted approach stands as our strongest defence. To bolster our resilience against the looming threat of Ransomware, we must implement these strategies and foster a culture of preparedness and Cyber Vigilance within our organisations. With the financial impact of these attacks rising, and the frequency of attacks surging, the time to act is now.
Cyber Security Insurance Rates Fall as Businesses Improve Their Security

Cyber insurance premiums are falling globally as businesses become more adept in curbing their losses from cyber crime. Insurance premiums to protect companies against cyber attacks rocketed in 2021 and 2022, as the COVID-19 pandemic drove cyber incidents. But premiums have been dropping in the past year. The cyber insurance market saw double digit price reductions in 2023/2024. Greater appetite by insurers to offer cyber insurance is also leading to price decreases. Ransom software works by encrypting data. Typically, hackers offer a pass code to victims of an attack, enabling them to retrieve the data in return for cryptocurrency payments. Business interruption is usually the biggest cost following a cyber attack, but businesses are able to reduce those costs with better back-up systems, such as through the use of cloud providers. Most cyber insurance business is in the United States, but growth in the $15 billion global cyber insurance market is likely to be fastest in Europe in the next few years, given lower penetration levels currently. Smaller firms are less likely to buy cyber insurance, partly due to lack of awareness of cyber risk.
7 Common Security Attacks in The OSI Layer Model
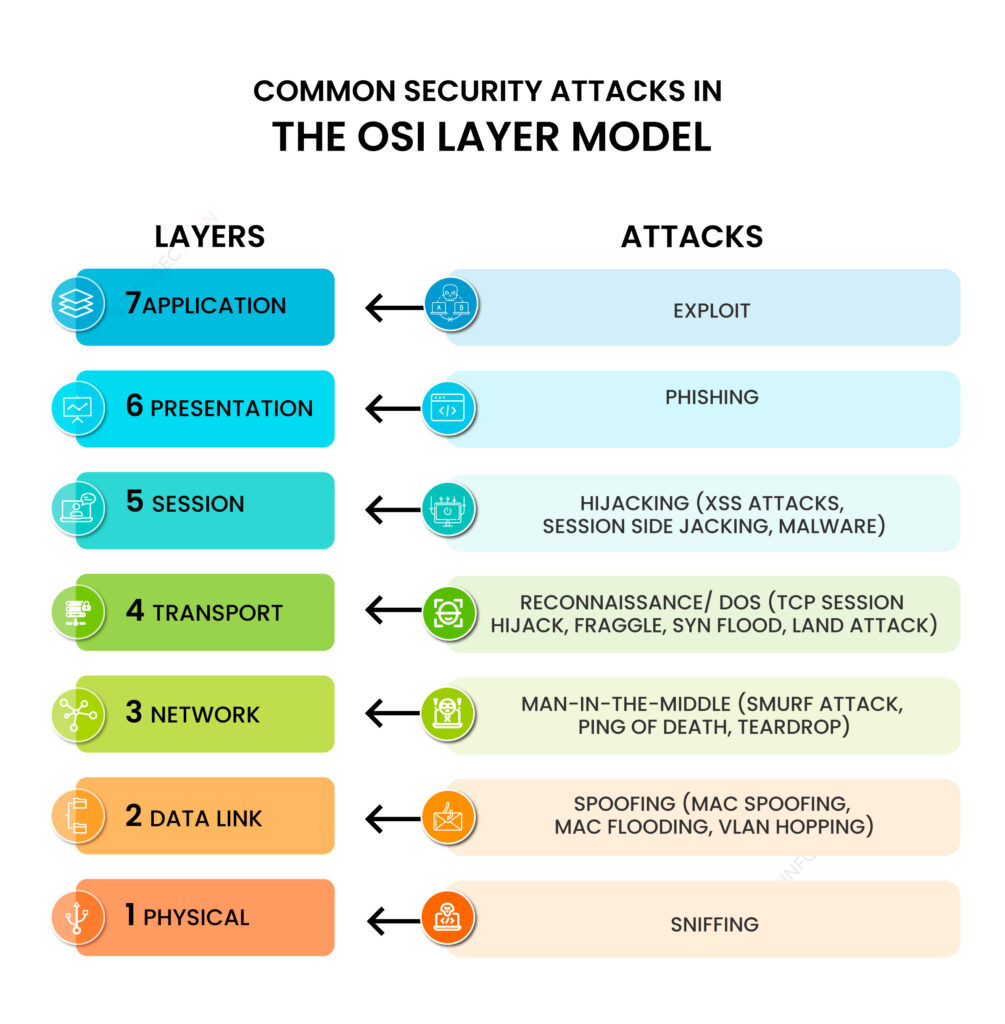
1) Sniffing attacks consist of intercepting data using a packet sniffer application. Then, if the captured packets are not encrypted, the packet sniffer can be used to read them. This allows attackers to analyze the network and gain information to corrupt it or even cause it to crash. 2) Spoofing attacks consist of a person or program falsifying data to identify as an authorized user or device. By impersonating authorized users or devices, attackers can bypass access control to systems, steal data and spread malware. 3) Man-in-the-middle attacks, abbreviated as “MitM attacks”, consist of an attacker placing himself between two communicating parties to monitor, relay and even alter the content of messages. 4) Reconnaissance attacks consist of gathering information about a system in order to identify its vulnerabilities. Although it was originally used as an ethical hacking technique to identify security loopholes and improve security, it has also become a mechanism to identify vulnerabilities before launching a cyberattack. 5) Hijacking attacks consist of intercepting and taking control of an established communication session either to access sensitive data or to gain unauthorized access to the targeted user’s computer or account. 6) Phishing attacks consist of deceiving individuals into revealing sensitive data through diverse techniques. It is one of the most commonly used cyberattacks nowadays and includes many types of attacks. 7) An exploit consists of taking advantage of vulnerabilities in software applications to gain unauthorized access and take control over a system, and perform diverse types of attacks, such as a denial-of-service attack.
New Phishing Campaign Deploys WARMCOOKIE Backdoor Targeting Job Seekers

Cybersecurity researchers have disclosed details of an ongoing phishing campaign that leverages recruiting- and job-themed lures to deliver a Windows-based backdoor named WARMCOOKIE. WARMCOOKIE appears to be an initial backdoor tool used to scout out victim networks and deploy additional payloads. The backdoor comes with capabilities to fingerprint infected machines, capture screenshots, and drop more malicious programs. The company is tracking the activity under the name REF6127. The attack chains observed since late April involve the use of email messages purporting to be from recruitment firms like Hays, Michael Page, and PageGroup, urging recipients to click on an embedded link to view details about a job opportunity. Users who end up clicking on the link are then prompted to download a document by solving a CAPTCHA challenge, following which a JavaScript file (“Update_23_04_2024_5689382.js”) is dropped. A crucial component of the campaign is the use of compromised infrastructure to host the initial phishing URL, which is then used to redirect victims to the appropriate landing page. The backdoor is designed to capture information about the infected host in a manner that’s similar to an artifact used in connection with a previous campaign codenamed Resident that targeted manufacturing, commercial, and healthcare organisations. While this attack does not utilize automated installation of malware, it does require users to engage with various prompts and clicks. However, this technique cleverly obscures the attacker’s true intent, exploiting the trust users place in familiar interfaces and common actions like opening email attachments.
Uncovering High Street Bank’s Mobile App & Online Security Gaps

In today’s digital age, Online & Mobile Banking have become the norm for millions of customers in the UK. However, a recent 2024 Report by the respected consumer magazine “Which?” has raised alarming concerns about the security measures implemented by some of the country’s major high street banks. The report scrutinized the Mobile App & Online Security Practices of several banks across Four Key Dimensions – Login Security (30%), Security Best Practices (30%), Account Management / Navigation (25%) & Logout Processes (15%). TSB, the Co-operative Bank & Lloyds Bank (includes Subsidiaries Halifax & Bank of Scotland) received particular criticism for apparent security lapses identified during this in-depth testing. TSB ranked lowest for mobile app security with a score of just 54%, while its Online Security Score of 67% was the second-lowest among Banks evaluated. Notably, the report flagged issues with the TSB app’s handling of sensitive user data, which could potentially be accessed by other apps on the same device. Additionally, User Credentials were stored in a manner susceptible to unauthorised access. The Co-operative Bank performed poorly in both Online (61% score) & Mobile App Security (57% score). Glaring gaps included a lack of mandatory two-factor authentication and failure to prevent customers from creating weak passwords. Perhaps most concerning was the ability for users to log in from multiple IP addresses concurrently without terminating previous sessions. While Lloyds Bank did not face specific Mobile App Security criticisms, its practice of not automatically logging out inactive users after 5 Minutes raised eyebrows. The bank defended this approach citing accessibility needs, but security experts warn it unnecessarily exposes accounts to potential misuse if left unattended. The Security weaknesses identified were preventable issues that should have been caught during the banks’ internal review processes and penetration testing. As an ex-member of HSBC’s Security Team (well done to the HSBC Team for being the Top-Ranked Bank for Mobile App Security) and ex-CISO of one of the biggest High Street Bank in Hong Kong, it is doubtful these lapses would have persisted through their security vetting. The report indicated that they are not isolated cases. The Mobile-Only Challenger bank Monzo failed on Security Best Practices, raising questions about their security investment and processes. It appears Monzo still has a long way to catch up to traditional High Street Banks in this critical area. In response, the implicated Banks acknowledged the need for prompt remediation while reiterating commitments to Cyber Security. Investing in robust security controls and expertise was stated as an ongoing priority to Balance Security, User Experience & Accessibility. As Online & Mobile banking becomes increasingly ubiquitous, safeguarding customer data must be paramount for financial institutions. The “Which?” Magazine findings serve as a wake-up call for high street banks to prioritize rigorous security practices and regain customer trust. Consumers deserve Assurance that their financial wellbeing is protected against the ever-evolving threats of Cybercrime.




